How to Install and Configure Gogs on Ubuntu 18.04
Updated on
•6 min read

Gogs is a self-hosted open-source git server written in Go. It includes a repository file editor, project issue tracking, and a built-in wiki.
Gogs is a lightweight application and can be installed on low-powered systems. If you are searching for an alternative to Gitlab with a much smaller memory footprint and you don’t need all the bells and whistles that Gitlab offers then you should definitely try Gogs.
This tutorial covers the steps to install and configure Gogs on Ubuntu 18.04. The same instructions apply for Ubuntu 16.04 and any other Ubuntu-based distribution.
Before You Begin
Gogs can use SQLite, PostgreSQL , or MySQL /MariaDB database to store all its data.
In this tutorial, we will use SQLite as the database of choice. If SQLite is not installed on your system you can install it by typing:
sudo apt install sqlite3For an additional layer of security, it is recommended to set up a basic firewall. You can follow the steps in our How To Set Up a Firewall with UFW on Ubuntu 18.04 guide.
Installing Gogs
We will install Gogs from binary. The installation is a pretty straight forward process.
Install Git
The first step is to install Git on your server. To do so, refresh the local package index and install the git package by running the following commands as sudo user :
sudo apt updatesudo apt install git
Verify the installation by displaying the Git version:
git --versiongit version 2.17.1
Create a Git user
Create a new system user to run the Gogs service by typing:
sudo adduser --system --group --disabled-password --shell /bin/bash --home /home/git --gecos 'Git Version Control' gitThe command will create the user and set the home directory to /home/git. The output will look something like below:
Adding system user `git' (UID 111) ...
Adding new group `git' (GID 116) ...
Adding new user `git' (UID 111) with group `git' ...
Creating home directory `/home/git' ...
Download Gogs binary
Visit the Gogs Download page
and download the latest binary for your architecture. At the time of writing, the latest version is 0.11.86, if there is a new version available change the VERSION variable in the command below.
Download the Gogs archive in the /tmp directory using the following wget command
:
VERSION=0.11.86wget https://dl.gogs.io/${VERSION}/gogs_${VERSION}_linux_amd64.tar.gz -P /tmp
Once the download is completed, extract the Gogs tar.gz file
and move it to the /home/git directory:
sudo tar xf /tmp/gogs_*_linux_amd64.tar.gz -C /home/gitRun the following command to change the ownership of the Gogs installation directory to the user and group git:
sudo chown -R git: /home/git/gogsCreate a systemd Unit File
Gogs comes with a Systemd unit file that is already configured to match our setup.
Copy the file
to the /etc/systemd/system/ directory by typing:
sudo cp /home/git/gogs/scripts/systemd/gogs.service /etc/systemd/system/Once done, start and enable the Gogs service:
sudo systemctl start gogssudo systemctl enable gogs
Verify that the service is started successfully:
* gogs.service - Gogs
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gogs.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2019-04-25 04:13:44 PDT; 9s ago
Main PID: 14376 (gogs)
Tasks: 8 (limit: 2319)
CGroup: /system.slice/gogs.service
`-14376 /home/git/gogs/gogs web
Install Gogs using the web installer
Now that Gogs is downloaded and running, it is time to finalize the installation through the web interface.
Open your browser, type http://YOUR_DOMAIN_IR_IP:3000 and a screen similar to the following will appear:
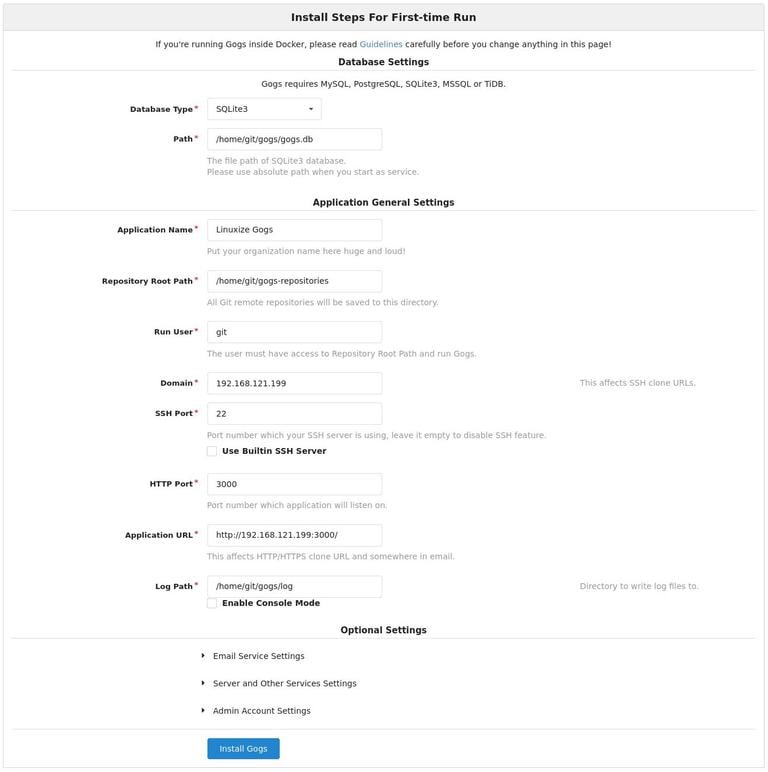
Database Settings:
- Database Type: SQLite3
- Path: Use an absolute path,
/home/git/gogs/gogs.db
Application General Settings
- Application Name: Enter your organization name
- Repository Root Path: Leave the default
/home/git/gogs-repositories - Run User: git
- Domain: Enter your domain or server IP address.
- SSH Port: 22, change it if SSH is listening on other Port
- HTTP Port: 3000
- Application URL: Use http and your domain or server IP address.
- Log Path: Leave the default
/home/git/gogs/log
Once done hit the “Install Gogs” button. The installation is instant and when completed you will be redirected to the login page.
Click on the “Sign up now” link.
The first registered user is automatically added to the Admin group.
That’s it. Gogs has been installed on your Ubuntu machine.
Configuring Nginx as SSL Termination Proxy
This step is optional but it is highly recommended. To use Nginx as a reverse proxy
you need to have a domain or subdomain pointing to your server public IP. In this tutorial, we will use gogs.example.com.
First, install Nginx and generate a free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate by following the guides below:
Once done, open your text editor and edit the domain server block file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/gogs.example.comserver {
listen 80;
server_name gogs.example.com;
include snippets/letsencrypt.conf;
return 301 https://gogs.example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name gogs.example.com;
proxy_read_timeout 720s;
proxy_connect_timeout 720s;
proxy_send_timeout 720s;
client_max_body_size 50m;
# Proxy headers
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# SSL parameters
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gogs.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/gogs.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gogs.example.com/chain.pem;
include snippets/letsencrypt.conf;
include snippets/ssl.conf;
# log files
access_log /var/log/nginx/gogs.example.com.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/gogs.example.com.error.log;
# Handle / requests
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
}
}
Restart the Nginx service for changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart nginxNext, we need to change the Gogs domain and root url. To do so, open the configuration file and edit the following lines:
sudo nano /home/git/gogs/custom/conf/app.ini[server]
DOMAIN = gogs.example.com
ROOT_URL = https://gogs.example.com/
Restart the Gogs service by typing:
sudo systemctl restart gogsAt this point, Gogs is configured and you can access it at: https://gogs.example.com
Configuring Email Notifications
In order for Gogs to be able to send notification emails, you can either install Postfix or use some transactional mail service such as SendGrid, MailChimp, MailGun or SES.
To enable email notifications, open the configuration file and edit the following lines:
sudo nano /home/git/gogs/custom/conf/app.ini[mailer]
ENABLED = true
HOST = SMTP_SERVER:SMTP_PORT
FROM = SENDER_EMAIL
USER = SMTP_USER
PASSWD = YOUR_SMTP_PASSWORD
Make sure you put the correct SMTP server information.
Restart the Gogs service for changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart gogsGogs also allows you to connect to Slack by creating web webhook and send notifications to your Slack channels .
Upgrading Gogs
To upgrade Gogs, several manual steps are required.
First stop the Gogs service:
sudo systemctl stop gogsRename the Gogs installation directory.
sudo mv /home/git/gogs{,_old}Download the latest Gogs version and move it to the
/home/gitdirectory:VERSION=<THE_LATEST_GOGS_VERSION>wget https://dl.gogs.io/${VERSION}/gogs_${VERSION}_linux_amd64.tar.gz -P /tmpsudo tar xf /tmp/gogs_*_linux_amd64.tar.gz -C /home/gitMake sure you change
VERSIONwith the actual Gogs release version.Copy
custom,data,logdirectories to the extracted directory using the following rsync command :sudo rsync -a /home/git/gogs_old/{custom,data,log,gogs.db} /home/git/gogs/Finally, start the Gogs service:
sudo systemctl restart gogs
That’s it.
Conclusion
This tutorial walked you through the installation and configuration of Gogs on Ubuntu 18.04. You can now create your first project and start using your new Gogs server.
If you have questions, feel free to leave a comment below.


